Capabilities of SQL SELECT Statements
Capabilities of SQL SELECT Statements
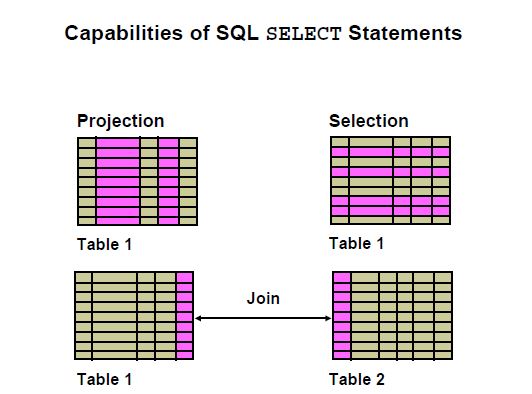
Topic Introduction: In this tutorial, we will discuss the Capacity of SQL statements. this is Projection, selection, and join.
A SELECT statement retrieves information from the database. With a SELECT statement, you can
do the following:
Projection: Select the columns in a table that are returned by a query. Select as few or as many
of the columns as required.
Ex.
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,DEPARTMENT_ID,SALARYFROM EMPLOYEES;
This query returns (EMPLOYEE_ID, LAST_NAME, DEPARTMENT_ID, SALARY) four columns from the employees' table with all data.
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,DEPARTMENT_ID,SALARY this is part of projection
Selection: Select the rows in a table that are returned by a query. Various criteria can be used to
restrict the rows that are retrieved.
Ex.
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,DEPARTMENT_ID,SALARYFROM EMPLOYEESWHERE DEPARTMENT_ID=10;
This query returns (EMPLOYEE_ID, LAST_NAME, DEPARTMENT_ID, SALARY) four columns from the employees' table with all data of department 10.
WHERE DEPARTMENT_ID=10 this is part of the selection.
Joins: Bring together data that is stored in different tables by specifying the link between them.
SQL joins are covered in more detail in the lesson titled “Displaying Data from Multiple Tables
Using Joins.”
Ex.
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,DEPARTMENT_NAME,SALARYFROM EMPLOYEES,DEPARTMENTSWHERE EMPLOYEES.DEPARTMENT_ID=DEPARTMENTS.DEPARTMENT_IDAND EMPLOYEES.DEPARTMENT_ID=10;
This query returns (EMPLOYEE_ID, LAST_NAME, DEPARTMENT_NAME, SALARY) four columns from the employees' table with all data of department 10. Here department names come from the departments table. For showing department names we need to use the departments table. and join with employees Table.
FROM EMPLOYEES,DEPARTMENTS
WHERE EMPLOYEES.DEPARTMENT_ID=DEPARTMENTS.DEPARTMENT_ID this is part of join


.png)
No comments